Last month astronomers announced that they had detected a tiny asteroid that had been captured by the Earth’s gravity well and had been sharing our orbit for a few years. Today, let’s talk about the smallest moons in the Solar System.


Last month astronomers announced that they had detected a tiny asteroid that had been captured by the Earth’s gravity well and had been sharing our orbit for a few years. Today, let’s talk about the smallest moons in the Solar System.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vUiGEfdJsK4 White dwarfs are usually about 60% the mass of the Sun, so it was a bit of a surprise when astronomers found one that was almost exactly twice that. What happens when white dwarfs merge? Download MP3| Download Raw Show with...
Pamela and Fraser discuss the implications of COVID-19 and it’s changes on the world, and what we all can do during this time.

We lost a bright star here on planet Earth last week. NASA mathematician Katherine Johnson passed away at the age of 101, after an incredible career of helping humans land on the Moon. If you saw the movie Hidden Figures, you’ll know what I’m talking about.
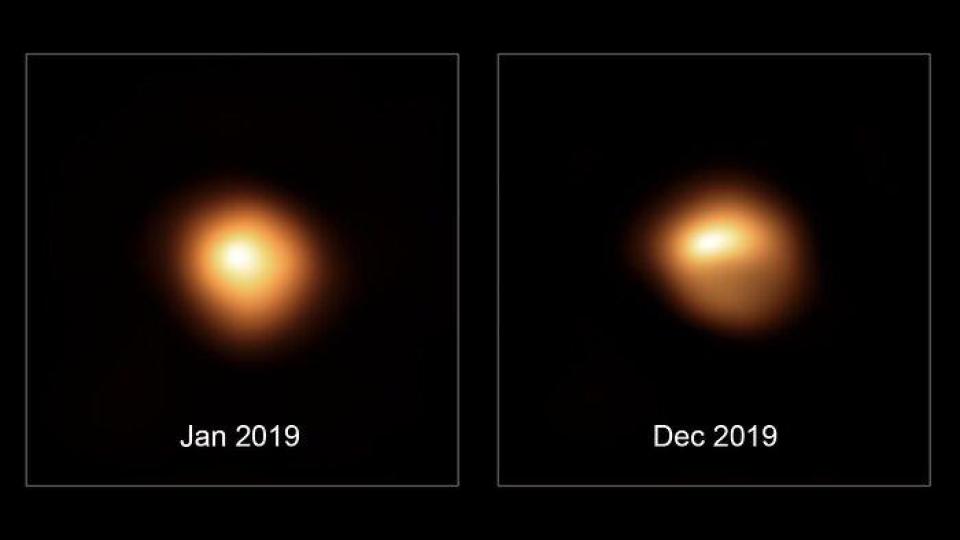

You might be surprised to hear that we’ve never done an episode of Astronomy Cast featuring Betelgeuse. Well, good news, this is that episode. Let’s talk about the star, why it might be dimming, and what could happen if it explodes as a supernova.
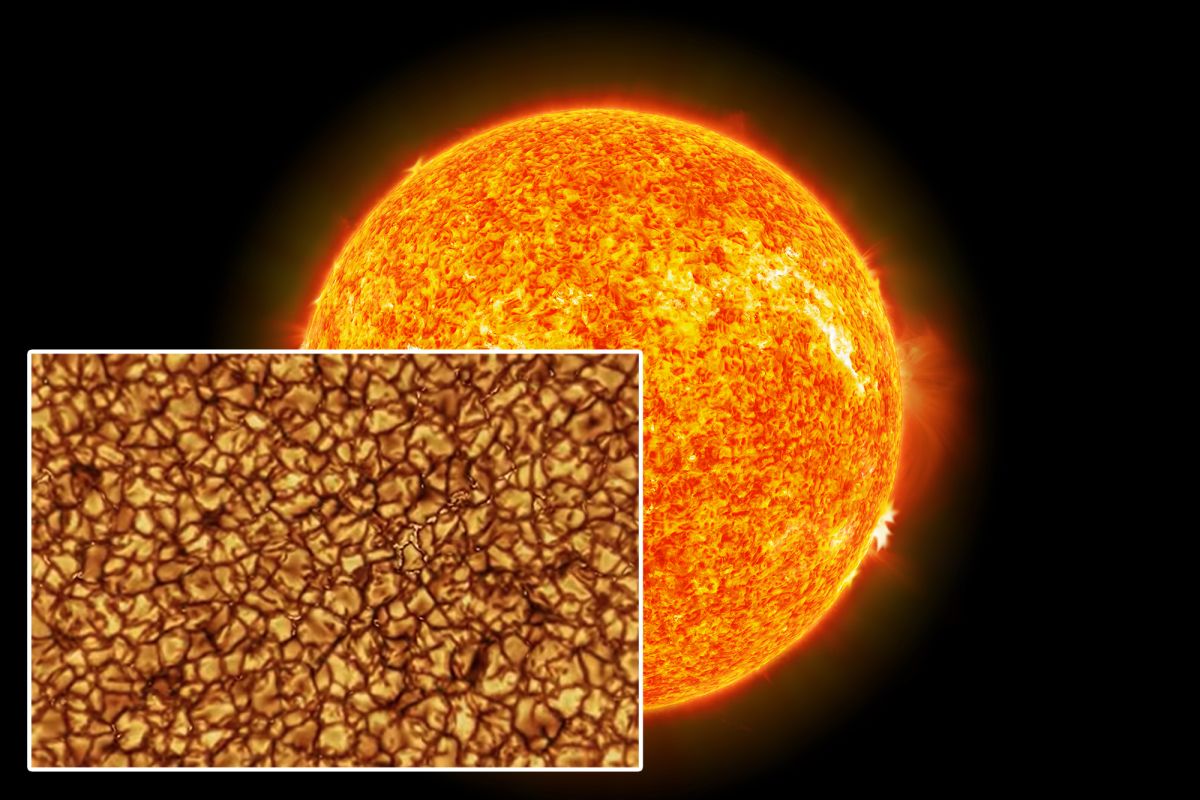
A brand new telescope has completed on Maui’s Haleakala, and it has just one job: to watch the Sun in unprecedented detail. It’s called the Daniel K. Inouye telescope, and the engineering involved to get this telescope operational are matched by the incredible resolution of its first images.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JJQFrgxlmus We've been following this story for more than a decade, so it's great to finally have an answer to the question, why was supernova 2006gy so insanely bright? Astronomers originally thought it was an example of a supermassive...
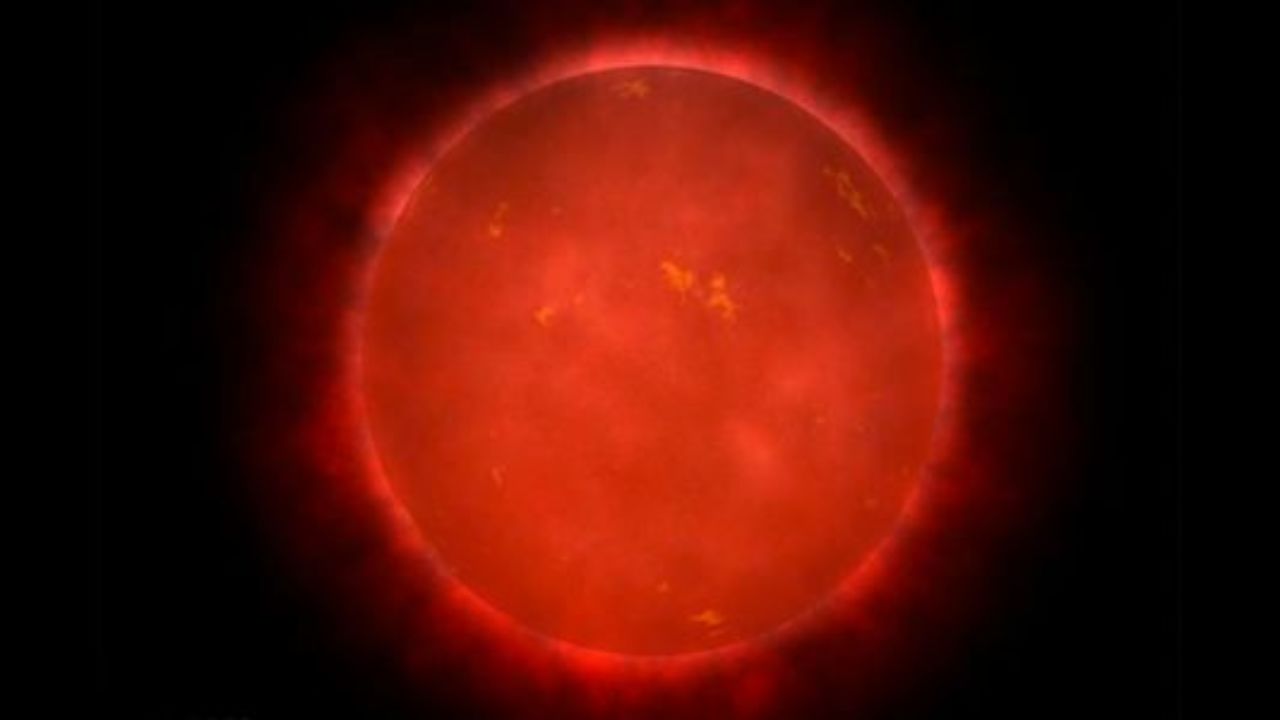

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wh1Ocfgmptc On the one hand, red dwarfs are the longest lived stars in the Universe, the perfect place for life to hang out for trillions of years. On the other hand, they're tempestuous little balls of plasma, hurling out catastrophic...
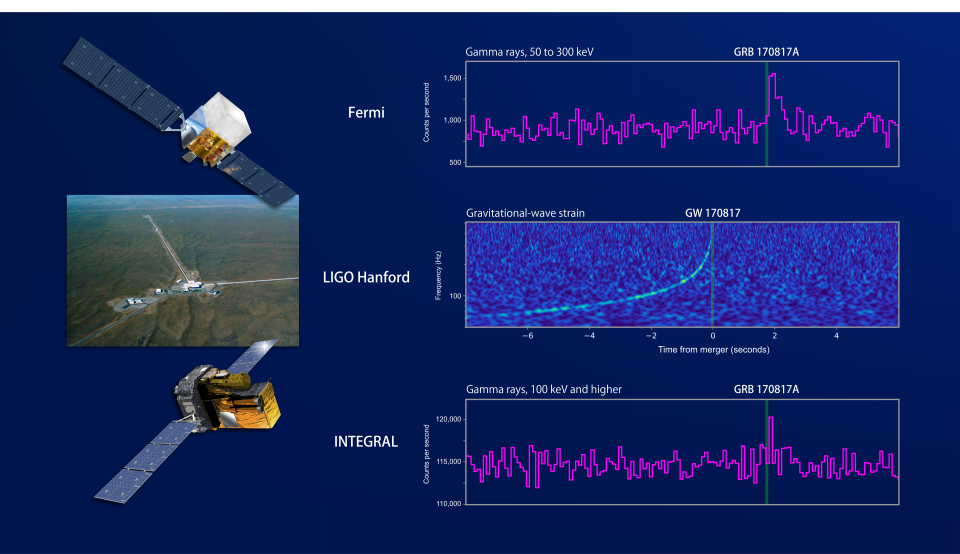
For the longest time astronomers could only study the skies with telescopes. But then new techniques and technologies were developed to help us see in different wavelengths. Now astronomers can study objects in both visible light, neutrinos, gravitational waves and more. The era of multi-messenger astronomy is here.
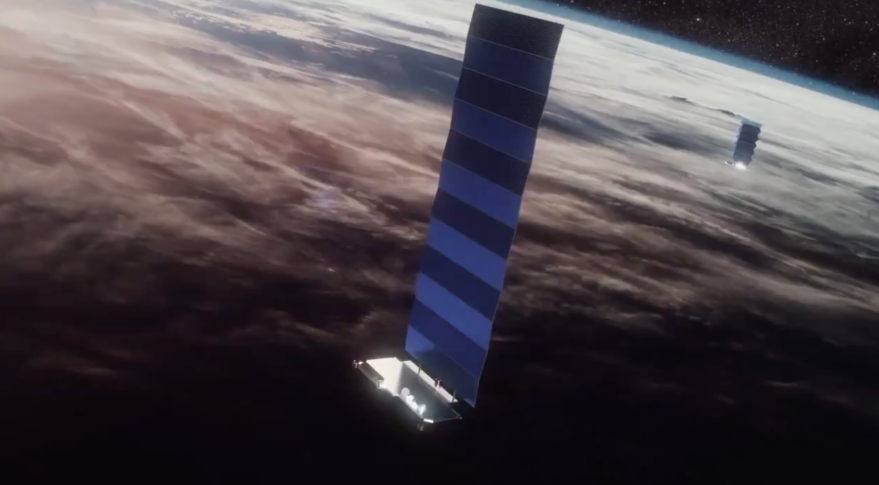

The other big issue at the AAS was the challenge that astronomy is going to face from all the new satellite constellations coming shortly. There are already 180 Starlinks in orbit, and thousands more are coming, not to mention the other constellations in the works. What will be the impact on astronomy, and what can we do about it?

This week we’re live at the American Astronomical Society’s 235th meeting in Honolulu, Hawai’i. We learned about new planets, black holes and star formation, but the big issue hanging over the whole conference is the protests and politics over the new Thirty Meter Telescope due for construction on Mauna Kea.
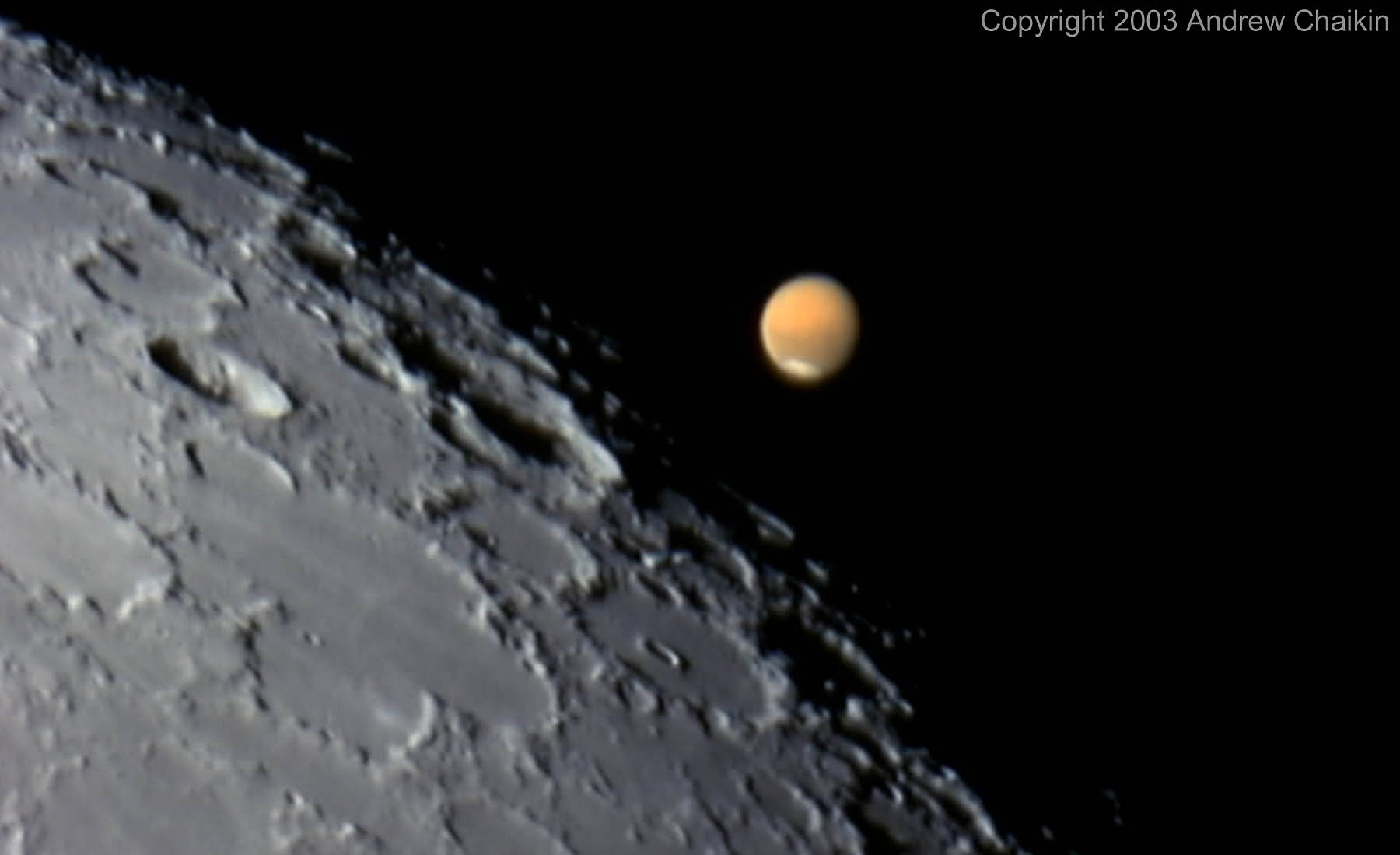

It’s hard to believe it, but we survived another trip around the Sun. Now it’s time to take the whole journey all over again, but with new news. Let’s take a look at some of the space and astronomy stories we’re looking forward to in 2020.
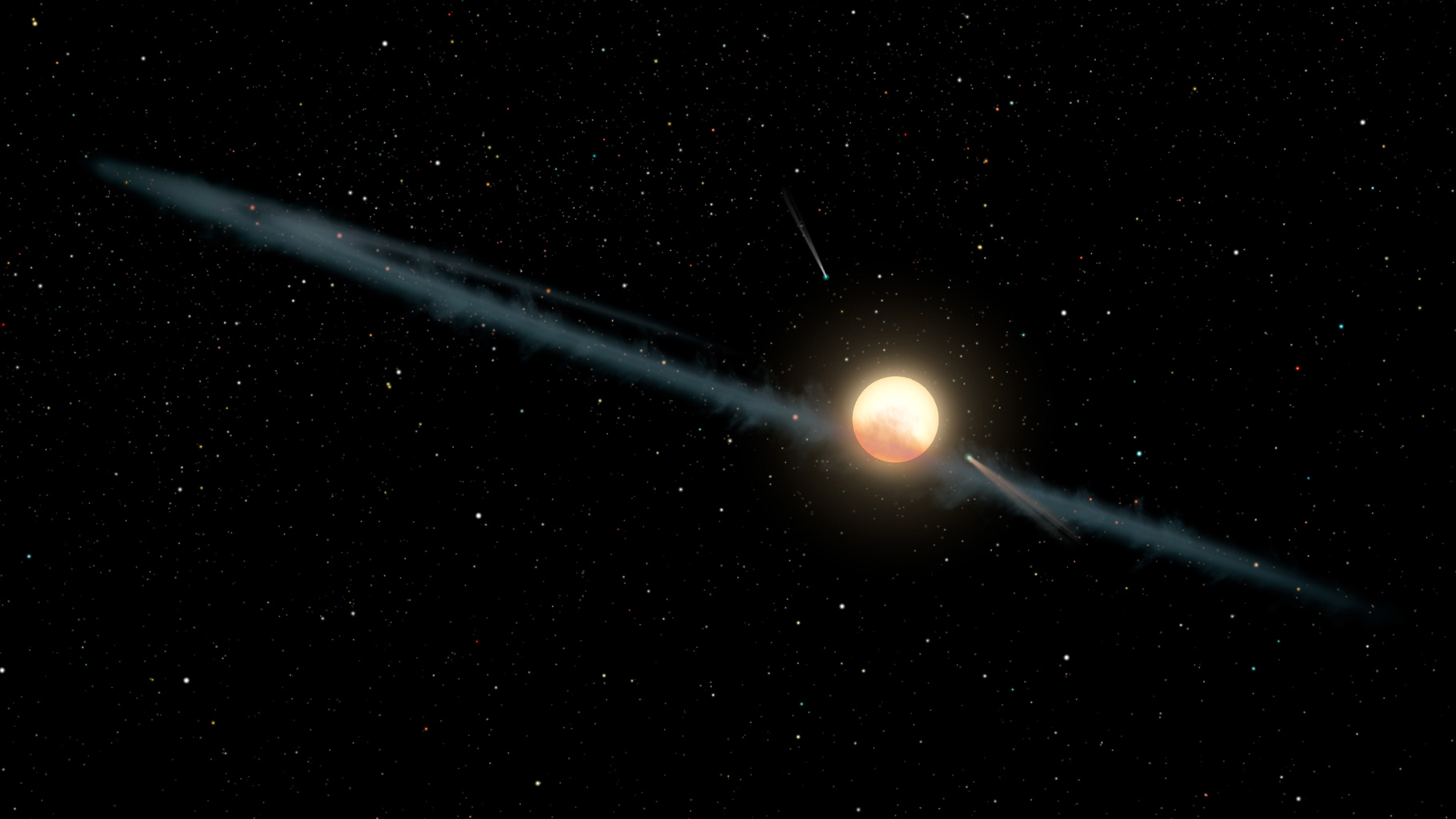

Huge surveys of the sky are finding more and more planets, stars and galaxies. But they're also turning up strange objects astronomers have never seen before, like Boyajian's star. Today we're going to talk about some unusual objects astronomers have discovered, and...
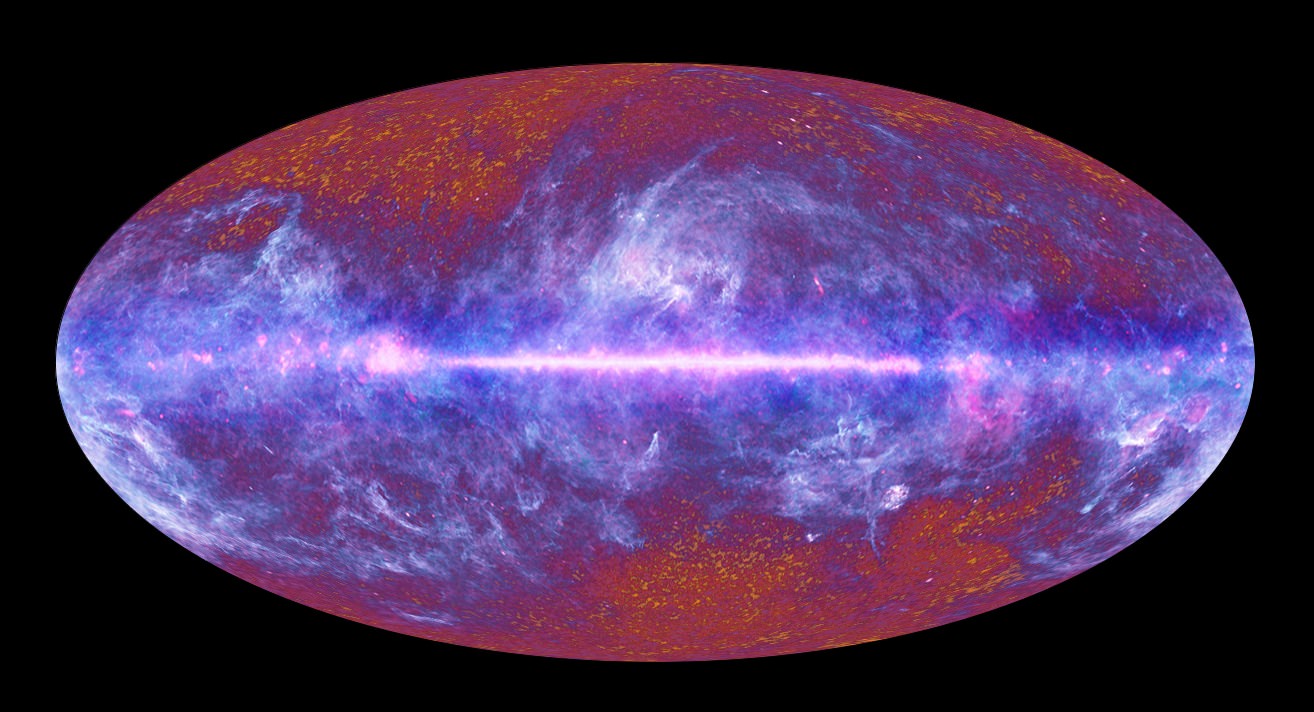
The Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation is the earliest moment in the Universe that we can see with our telescopes, just a few hundred thousand years after the Big Bang itself. What will it take for us to be able to fill in the missing gap? To see closer to the beginning of time itself?

Powerful observatories like Hubble and the Very Large Telescope have pushed our vision billions of light-years into the Universe, allowing us to see further and further back in time. But there are regions which we still haven’t seen: the Cosmic Dark Ages. What’s it going to take to observe some of these earliest moments in the Universe?
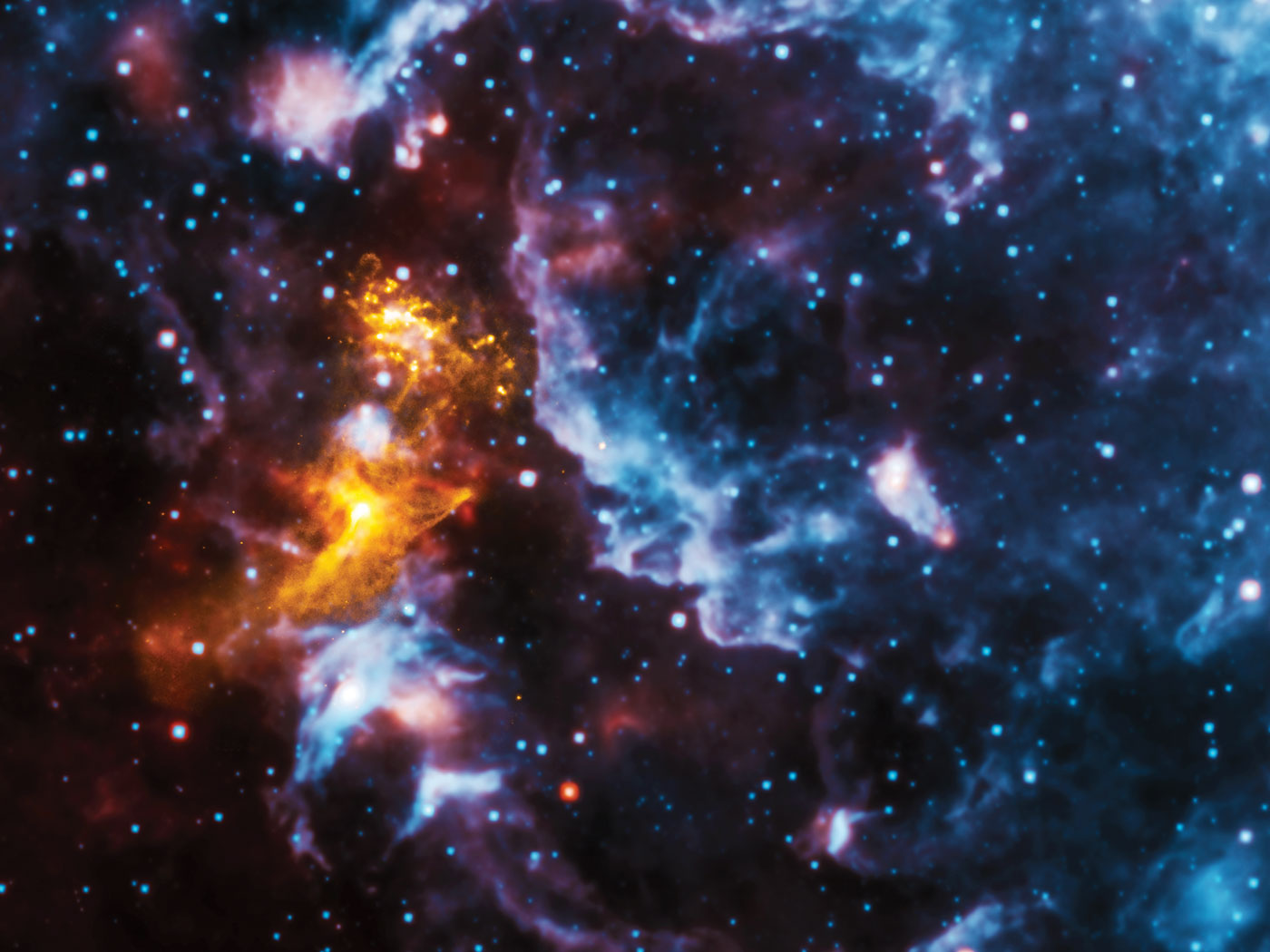

Last week we gave you an update on the formation of elements from the Big Bang and in main sequence stars like the Sun. This week, we wrap up with a bang, talking about the death of the most massive stars and how they seed the Universe with heavier elements.
The Universe started out with hydrogen and helium and a few other elements, but all around us, there are other, more proton-rich elements. We believe these heavier elements formed in stars, but which stars? And at what points in their lives? Today we’ll update our knowledge with the latest science.

Few sciences have been able to take advantage of the power of computers like astronomy. But with all this computing power, you might be surprised to learn how important a role humans still play in this science.
Before we discovered other planets, our Solar System seemed like a perfectly reasonable template for everywhere. But now we see massive planets close to their stars, which leads you to the question, how does it all get there. Do the planets form in place or do they migrate around?

Things used to be so simple. Comets were snowballs from the outer Solar System, and asteroids were rocks from the inner Solar System. But now everything’s all shades of grey. Astronomers have found asteroids that behave like comets and comets that behave like asteroids.

Once again, another place where the Universe is going to make this difficult for us. Proving, once and for all that there’s alien life on another world. It should be straightforward, look for biosignatures, but it looks like there are natural sources that could explain almost any chemical we could hope to search for.
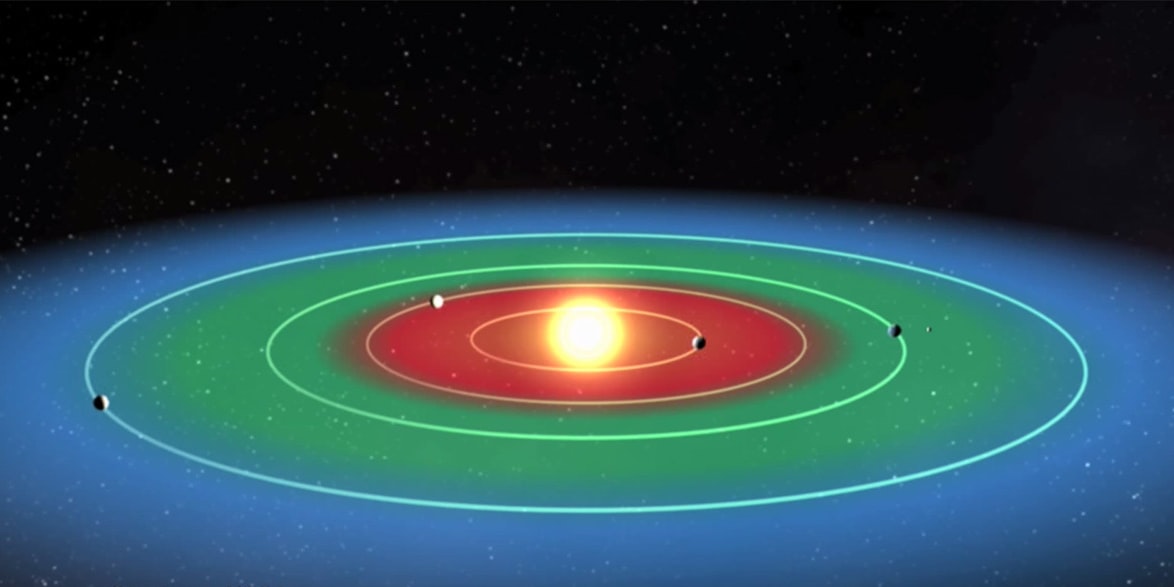
Our series on Universe weirdness marches on. This week we take a look at the habitable zone, and how things aren’t as simple as we thought.
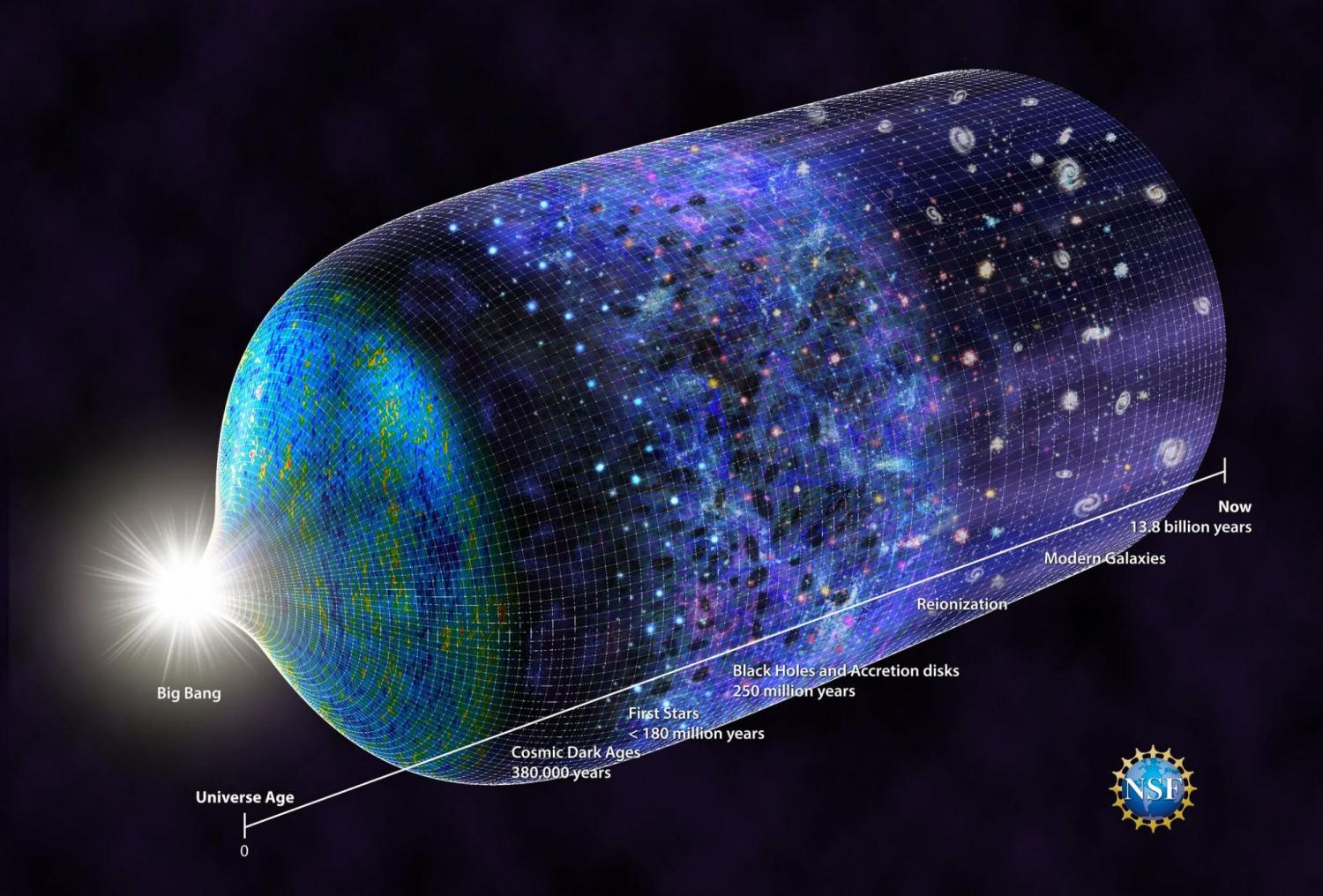
Our series on Universe weirdness continues, this time we learn how astronomers are struggling to make sense of the age of the Universe.
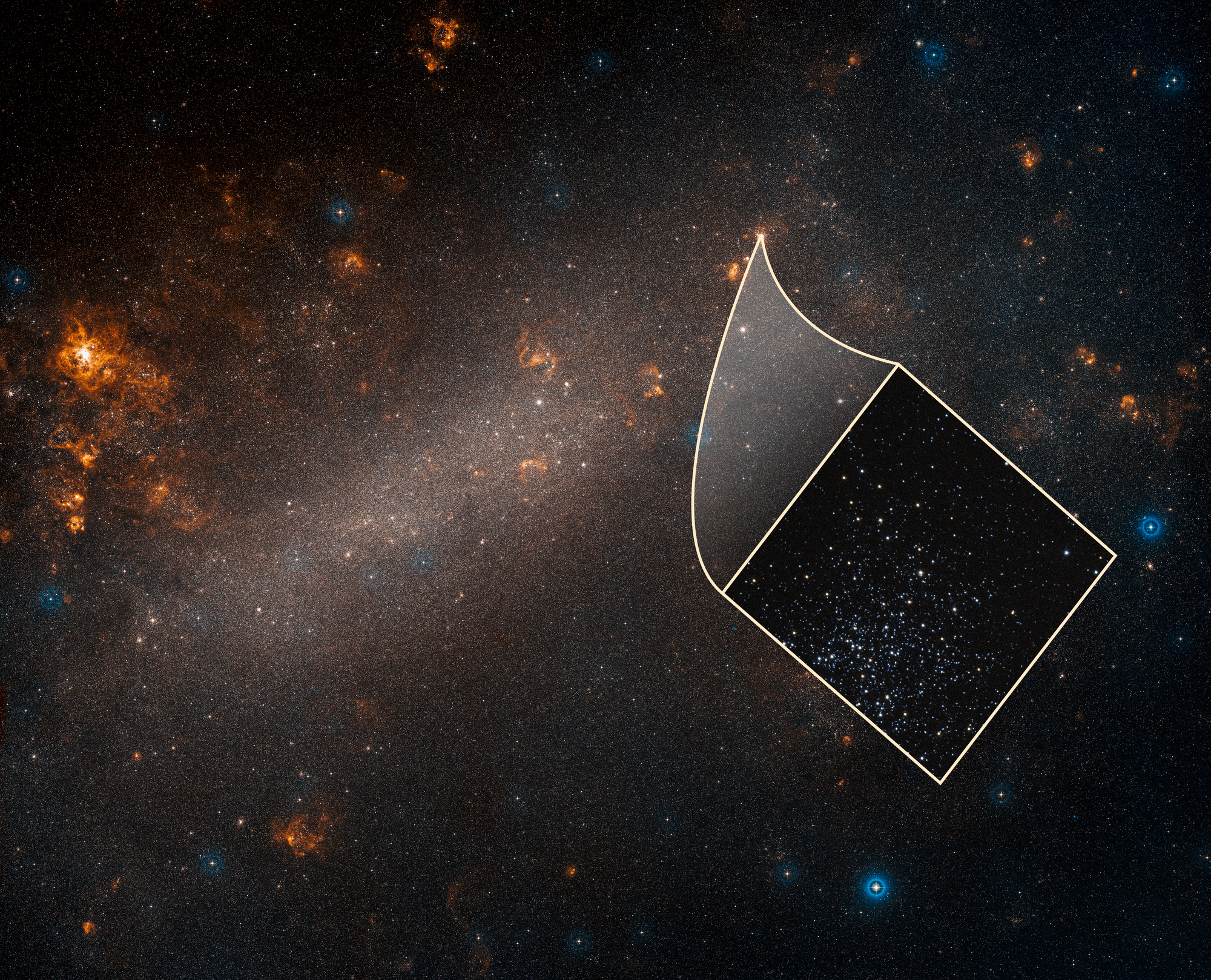

Just when the Universe was starting to make sense, the cosmos throws a curveball at us. Astronomers have been trying to accurately measure the expansion rate of the Universe as far back as Hubble. It’s been tough to nail down, and now astronomers are starting to figure out why.

As astronomers started to discover planets orbiting other stars, they immediately realized that their expectations would need to be tossed out. Hot jupiters? Pulsars with planets? We’re now decades into this task, and the Universe is continuing to surprise us.