What can we hope (or dread) to see in 2025? Today we’re gonna talk about the upcoming space stories for 2025 that we’re looking forward to.


What can we hope (or dread) to see in 2025? Today we’re gonna talk about the upcoming space stories for 2025 that we’re looking forward to.
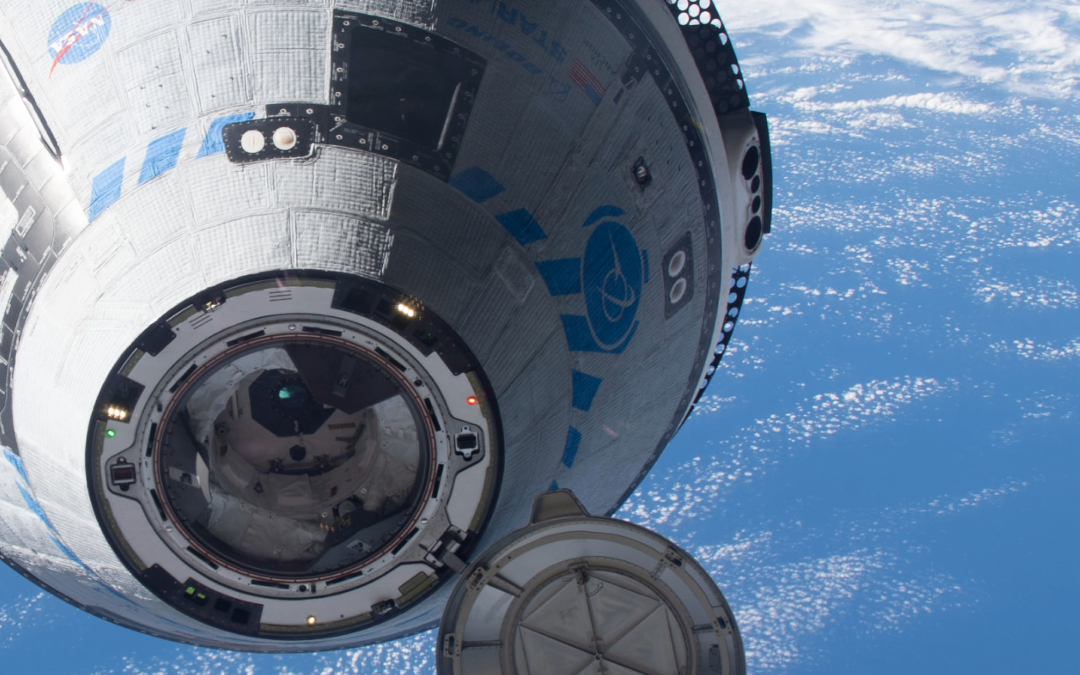

Starliner S2.1 docking on May 20, 2022 (NASA) Prior to recording their exoplanets episode, Fraser and Pamela discussed their wild week of space flight news and discussed their concerns about the Starliner and StarShip programs. This is particularly timely as we...

In this bonus episode, we bring you behind the scenes audio from our June 10 pre-show discussion about the “far too much news” that occurred the week of June 3, 2024. Check out the original recording on YouTube here. This episode was sponsored by Mint Mobile.

In the olden days, NASA developed its missions using a variety of in-house engineers and external suppliers. As more commercial companies are targeting the Moon, NASA is working with partners to deliver its payloads to the lunar surface.
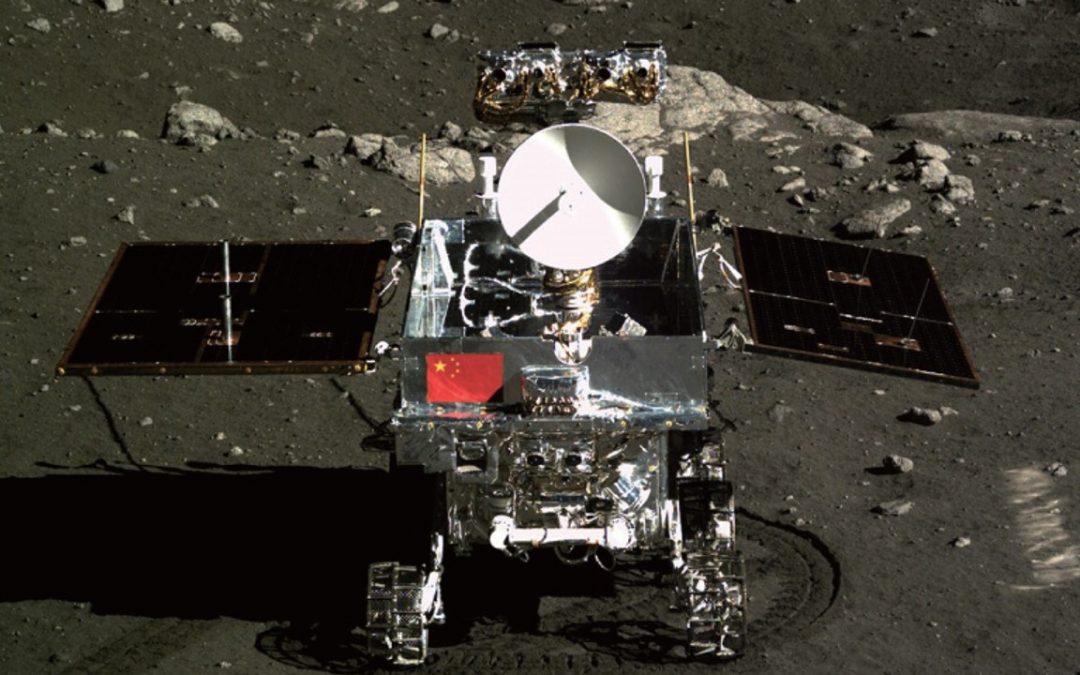

We’re so familiar with NASA’s exploration efforts in space, but you might be surprised to learn that China launches almost as many rockets as the US. They’ve got their own space exploration program that could soon bring humans to the surface of the Moon. Let’s give a brief overview of China’s space exploration plans.
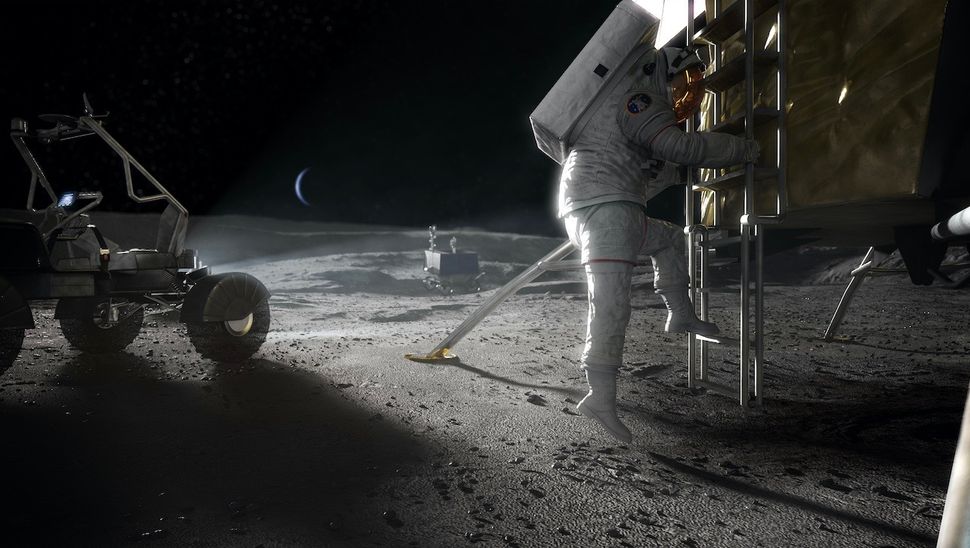

With Artemis 1 completing its robotic flight around the Moon, we know that the SLS works. Next comes Artemis 2, with a crew of astronauts flying past the Moon. If that’s successful, we could see humans set foot on the Moon in December 2025. But there is a long list of challenges to consider that could delay things considerably. Go or no go for launch?

Last week we looked back at some of the ideas that science has changed its mind about. This, we look forward, into the future, at some of the big ideas that astronomers are making progress in. What space science are we looking forward to?

Once again, we’ve reached the end of a season here on Astronomy Cast, and it’s time for the summer hiatus. But the Universe never takes a break. What can we expect to happen over the summer while we’re catching up on our reading, building our gardens and planning for Season 17
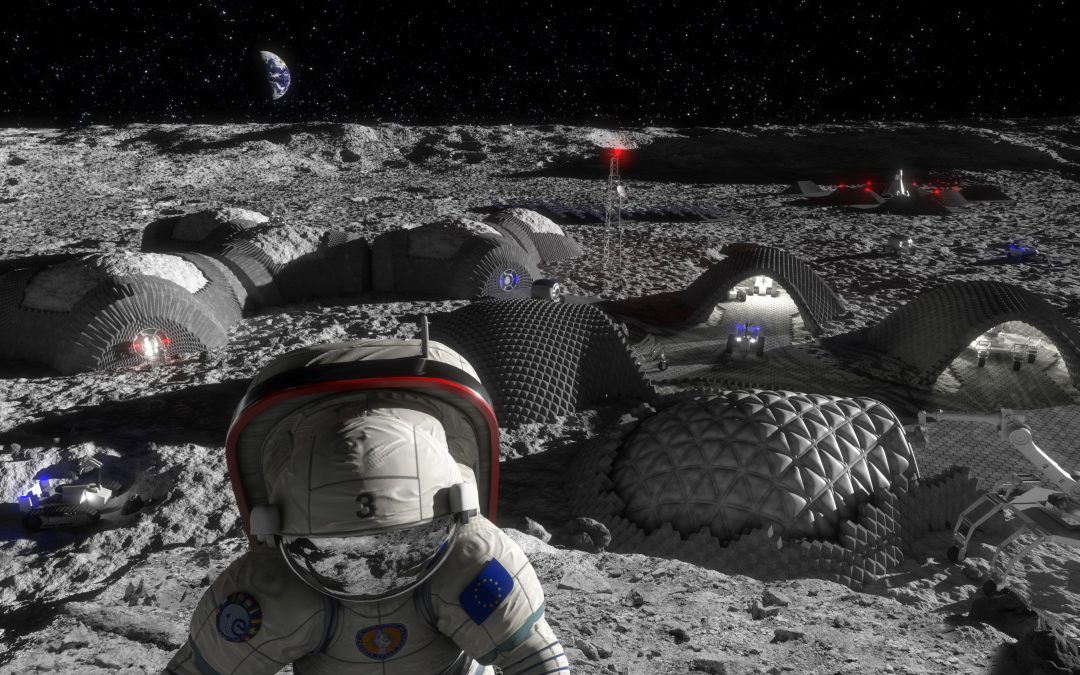
We’re going back to the Moon. In the next few years humans will set foot on the Moon again, ideally this time to stay. But this will be different than the Apollo era, going to the scientifically fascinating, and difficult southern pole of the Moon. What needs to be done to prepare the way back to the Moon?
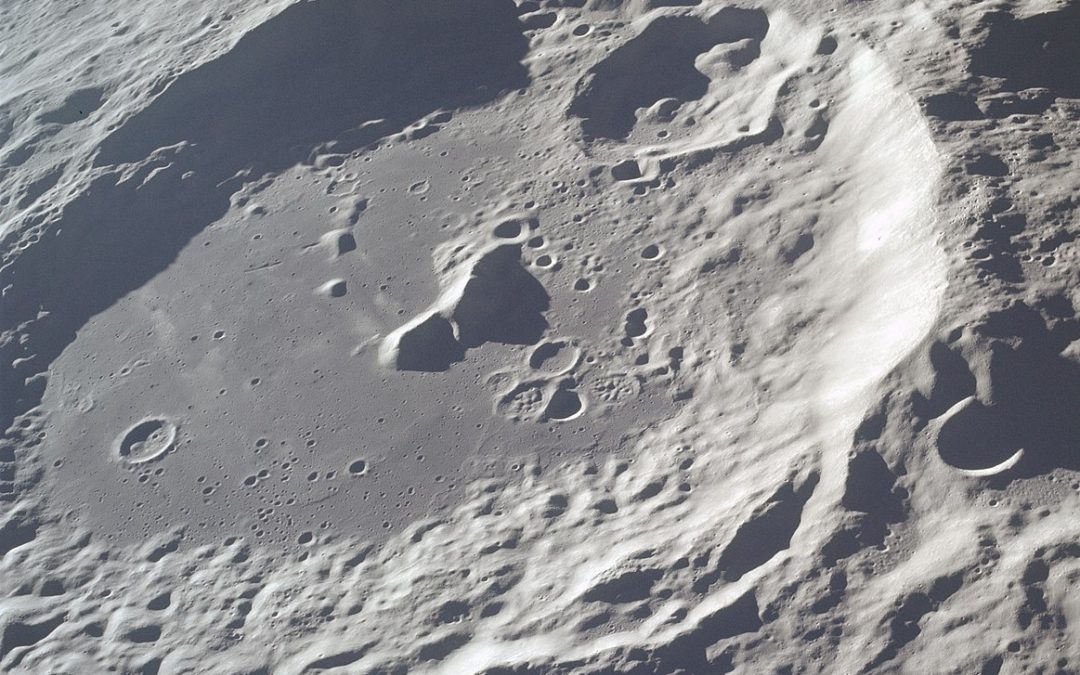

The permanently shadowed craters on the Moon are the focus of so much research. That’s because they seem to contain vast reserves of water ice. Water we could use for oxygen, propellant and so much more, but also, to help us understand where the Earth’s water came from.
Launching satellites from Earth is counter-productive. You’ve got to make a satellite that can handle Earth gravity, then the brutal flight to space, then deployment in orbit. What if you could build your spacecraft in space?

Last week we talked about the laws that govern space exploration. This week the rubber hits the road. What are the consequences for actually breaking these rules? Are they really going to stop anyone?

The Universe was inaccessible for most of human history, but the first tentative steps to space in the 20th century made humanity realize that science fiction was becoming science reality. New rules would have to be written to govern how we used this limitless expanse. Today we’ll talk about the Outer Space Treaty of 1967.

We’re recording this episode on Halloween, so how could we resist but take advantage of this opportunity. Space is already terrifying enough, you know, with the vast endless emptiness, incomprehensible mysteries, and uncaring coldness. But here are some scary stories to spook it up a notch.
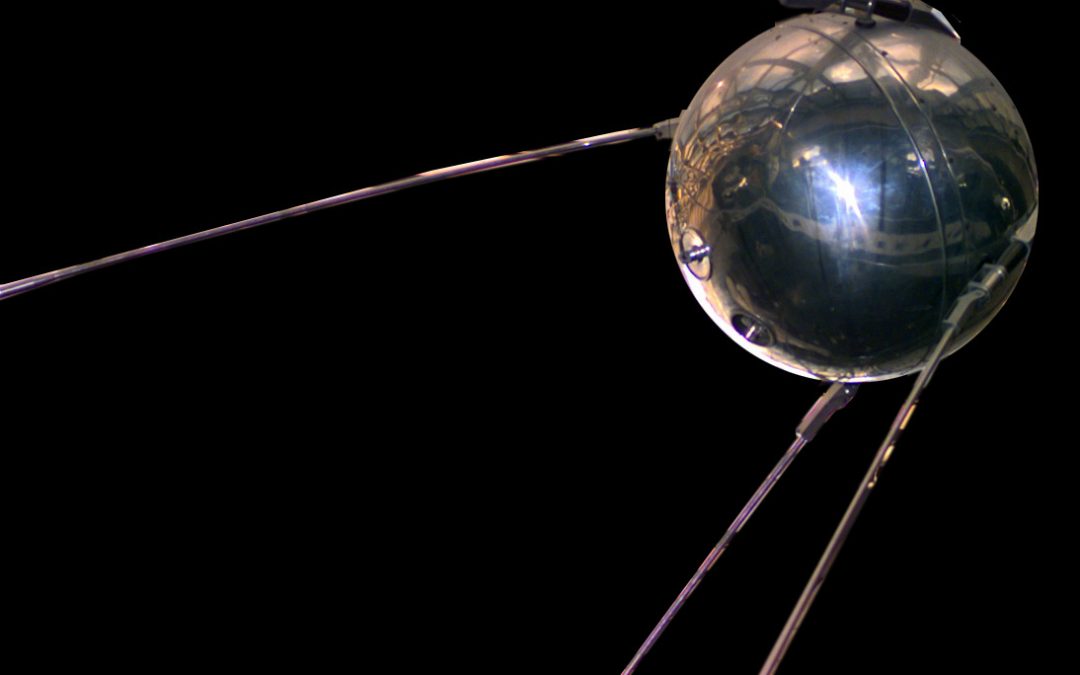

It’s been about 65 years since the Soviets launched the first orbital satellite into low Earth orbit: Sputnik 1. Now there are thousands of satellites in orbit, with tens of thousands on the way. Let’s look at the impact that Sputnik had on the history of spaceflight.
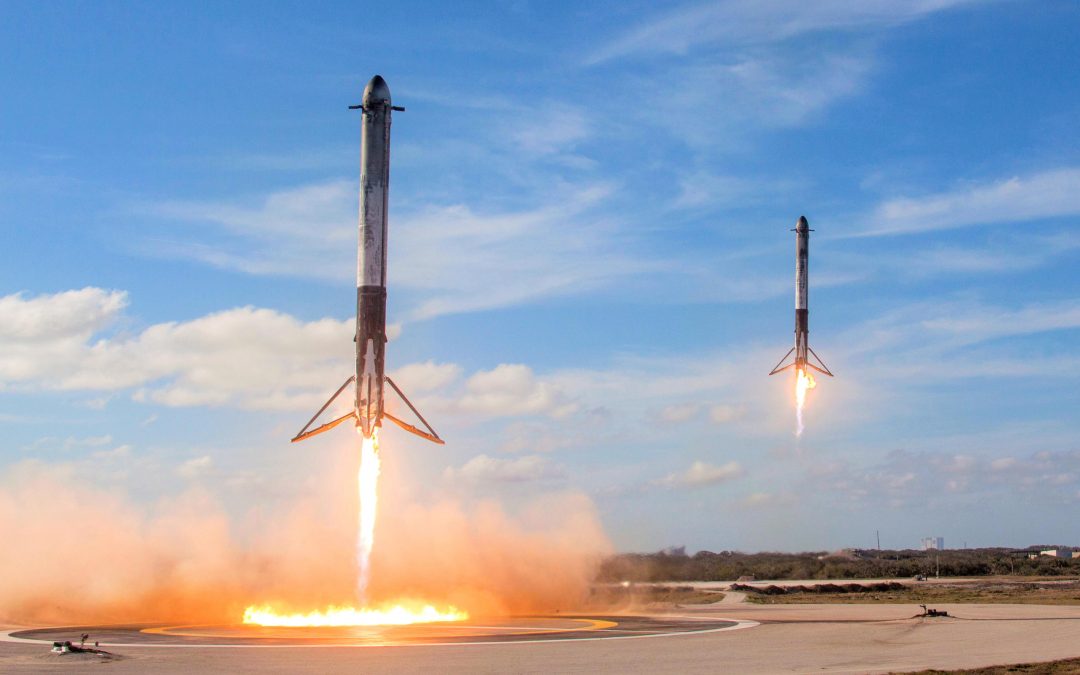

Last week we talked about how single-use rocketry has changed over time, and the role it still plays in launching payloads into orbit and beyond. Today, we’ll address the stainless steel elephant in the room and talk about the shift to reusability.
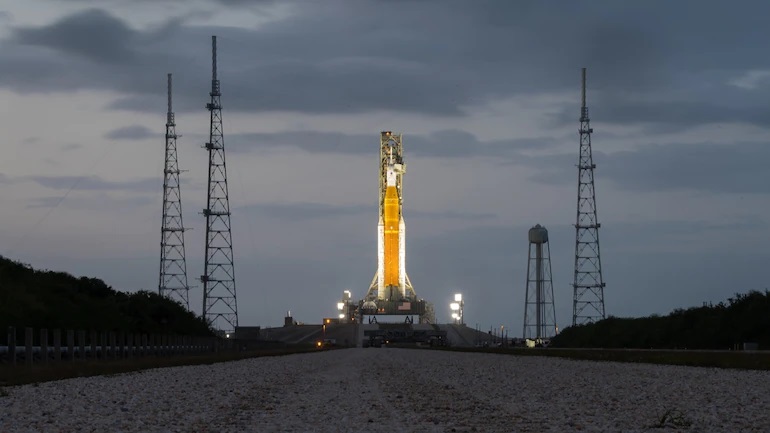

On the day that we’re recording this, NASA’s Space Launch System is about to blast off. But everyone is expecting it’ll be delayed to October. When it does launch, it’ll be the most powerful rocket on Earth. Well, until Starship blasts off. Are we about to see the end of single-use rockets and enter the era of reusable rocketry?

Have you ever noticed that significant space and astronomy events seem to happen during holidays? It’s not a coincidence, there’s actually a reason why. Today we’ll talk about some of the key events that happened during holidays.

We always say that we’re living in golden age of space and astronomy, but it feels like things are just accelerating. What does the long-term future hold for our place in the Universe?
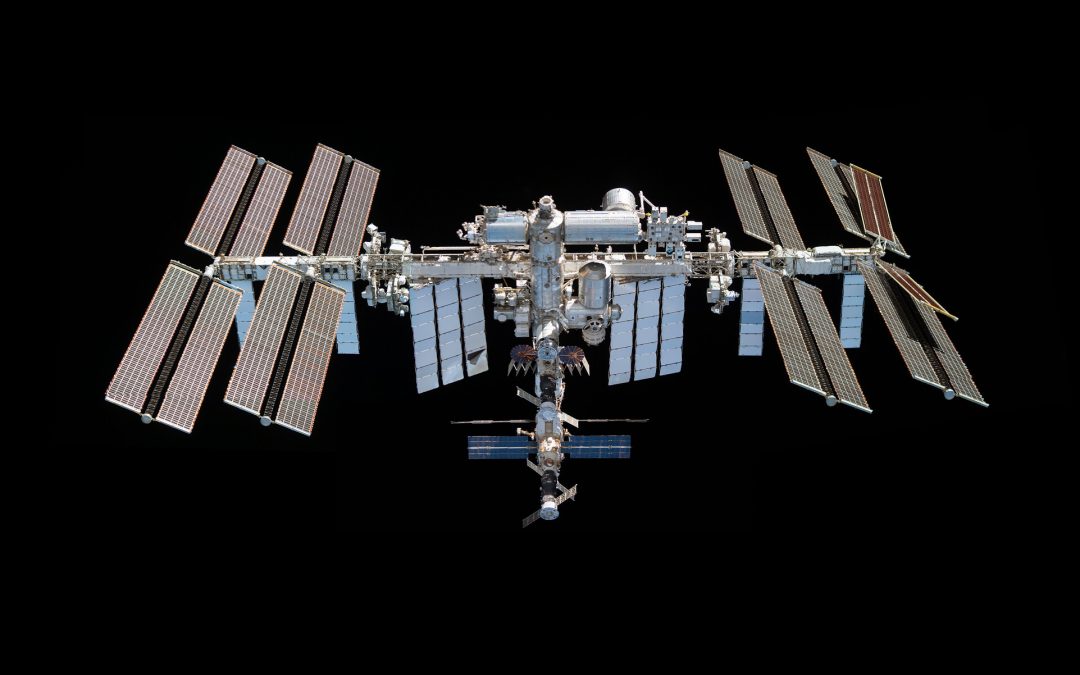

The International Space Station has been continuously inhabited for over 20 years now, serving as a peaceful collaboration between space-faring nations. But it’s a machine, and it’s getting old. In addition, the Russian invasion of Ukraine has made things complicated. What’s the future for the ISS?
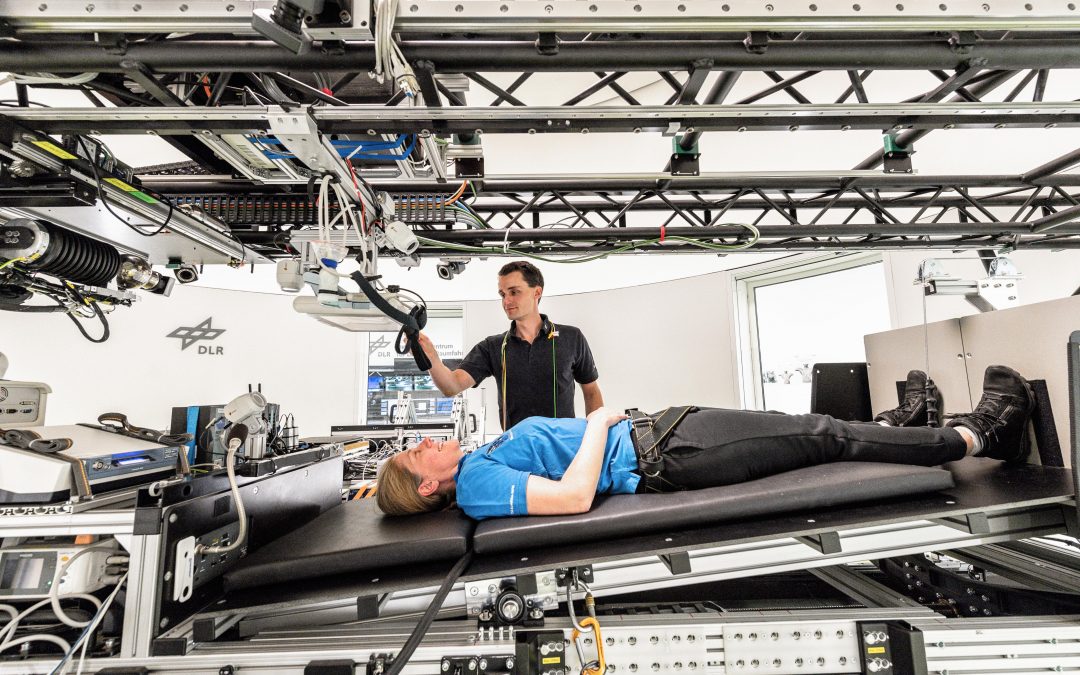

Although humans have never actually been to Mars, explorers have simulated many aspects of Mars missions here on Earth. There are missions under the ocean, on the tops of volcanoes, in the harsh Canadian north, and even in bed that simulate the limitations of spaceflight, and teach us many of the lessons to prepare us for the real thing.

In a rare moment of weakness, Pamela has decided she’s open to the possibility that a future exists. That missions, telescopes and spacecraft are going to be built and they’re going to do some science. Today we’ll talk about what we’re looking forward to before she changes her mind and ruins Fraser’s naive optimism for the future.

We’ve reached the end of 2021, and this is the last episode of the year. Let’s look back at the big space events of the last year and talk about what we’re looking forward to in 2022.

Good news! Over the next few years, we’re going to see a flotilla of new missions headed to Jupiter and Saturn. Why aren’t we seeing more missions to the outer planets, like Uranus and Neptune? It turns out, those places are far away. Today let’s talk about the challenge of exploring the outer Solar System.

The Moon is about to become a very busy place, with multiple countries and private companies planning missions in the next few years. It’s been decades since the Outer Space Treaty was negotiated. It’s time for the Artemis Accords.