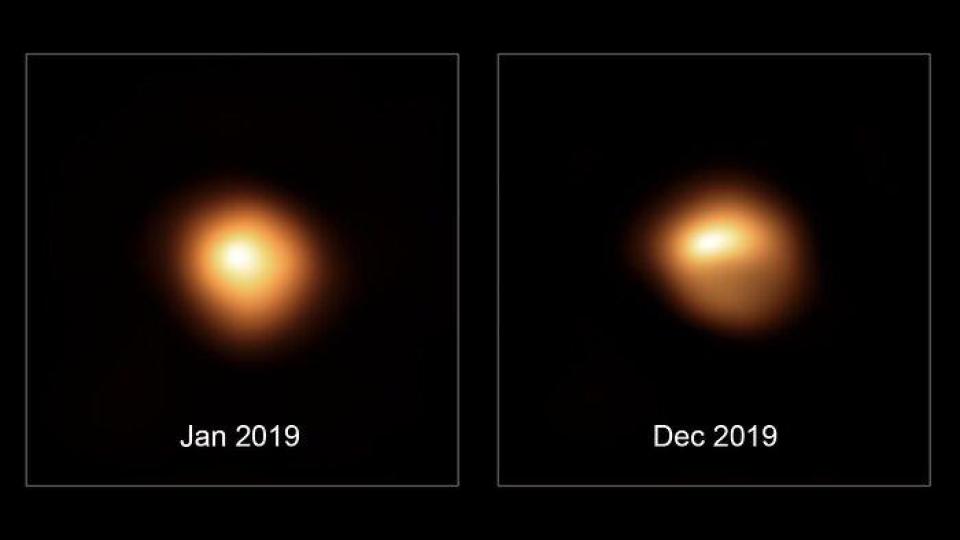
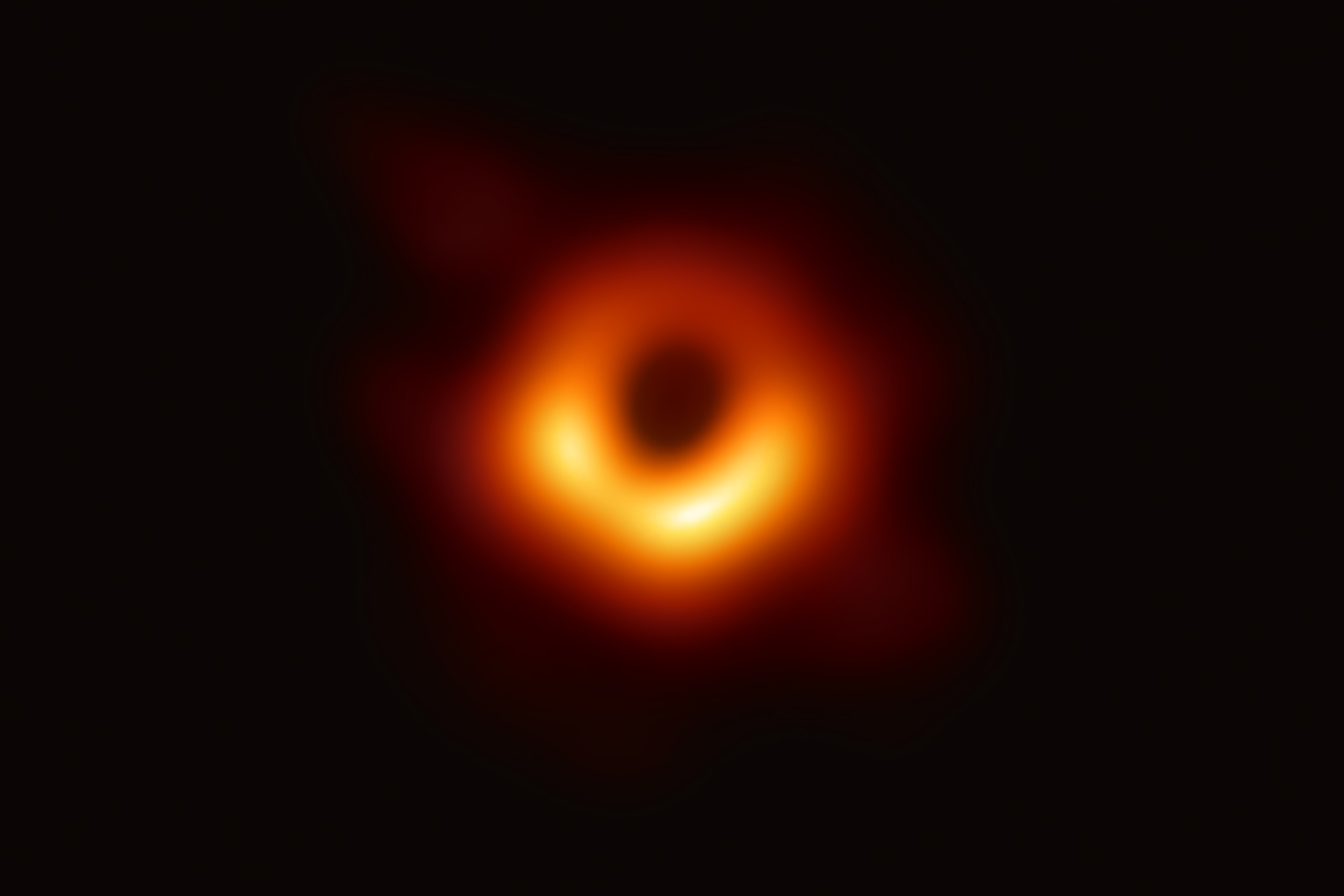
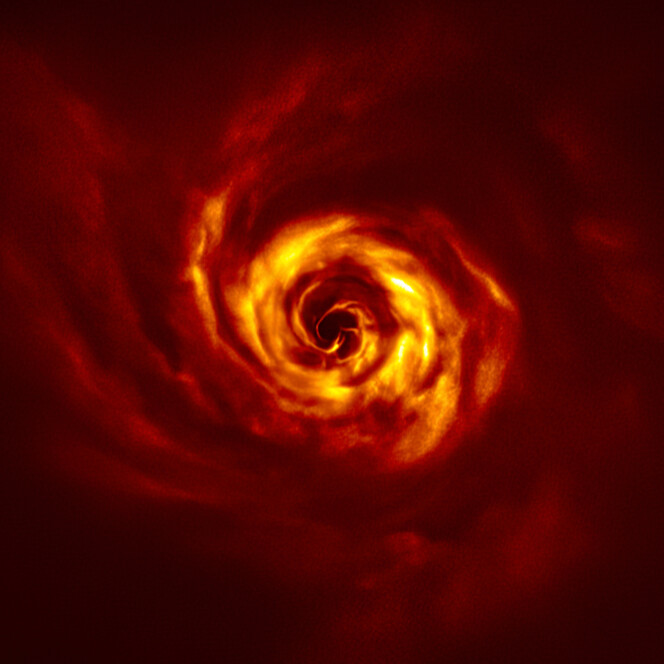
We’re all looking forward to the next generation of exoplanetary research, where we get to see pictures of planets directly. But astronomers are already making great strides in directly observing newly forming planets, helping us understand how our Solar System might have formed.