Several of the planets and moons in the Solar System are in orbital resonance, orbiting in a geometric lockstep. And not just the Solar System, astronomers have found the same resonances in other star systems.
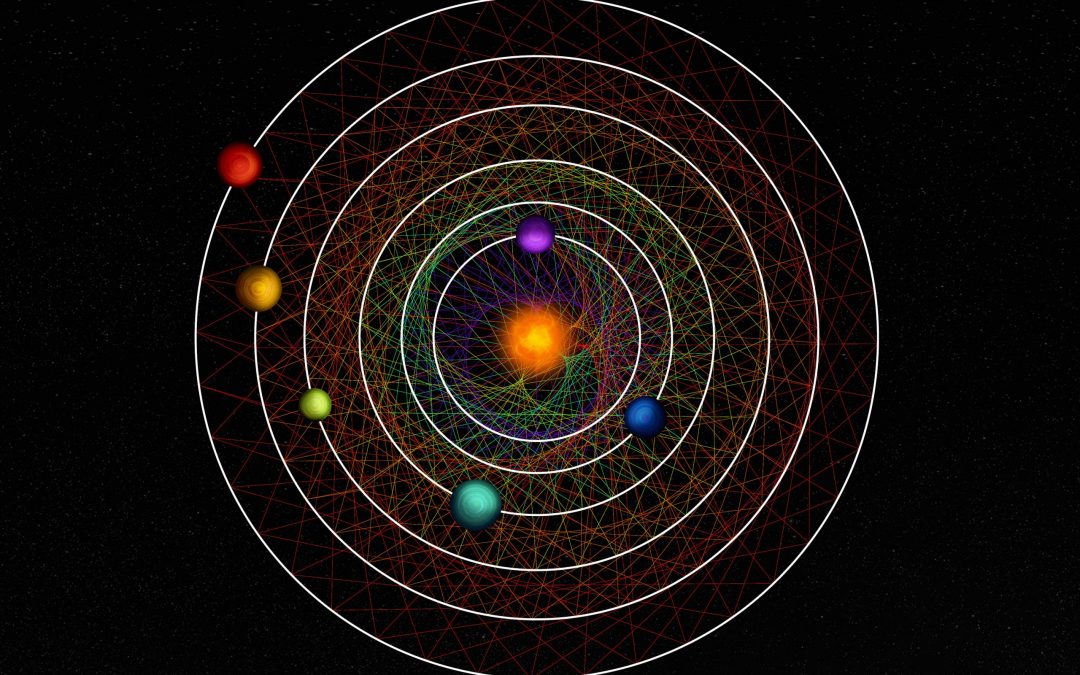

Several of the planets and moons in the Solar System are in orbital resonance, orbiting in a geometric lockstep. And not just the Solar System, astronomers have found the same resonances in other star systems.
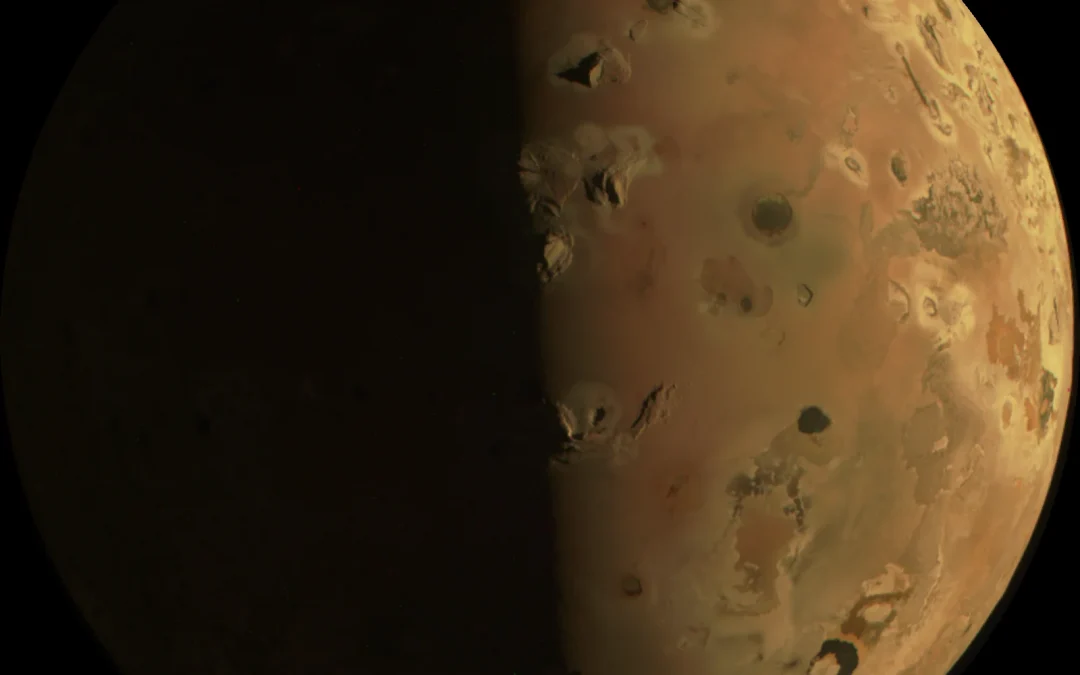
Last week was one of the most exciting meetings we’ve seen from the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, with hundreds of announcements and discoveries from various missions. One theme kept coming up, the Solar System is more volcanically active than we thought. Today, we’ll explore volcanism on other worlds.

You’ve probably heard that the best kind of science is peer-reviewed research published in a prestigious journal. But peer review has problems of its own. We’ll talk about that today.
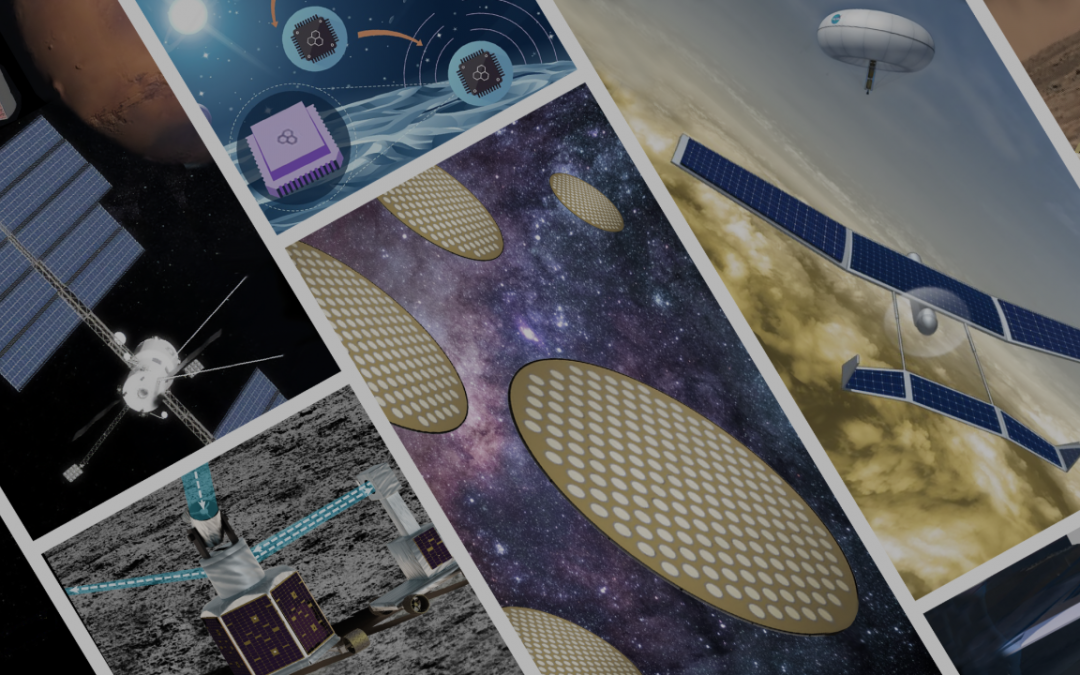

NASA works on many missions using tried and true technology, but they also invest in creative ideas that could drive the future of space exploration. It’s called NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concepts or NIAC.

In the olden days, NASA developed its missions using a variety of in-house engineers and external suppliers. As more commercial companies are targeting the Moon, NASA is working with partners to deliver its payloads to the lunar surface.

Last week we learned that Russia might be planning nuclear weapons to take out satellites in space. What is the current and future possibility of weapons in space and what are the treaties designed to prevent them?
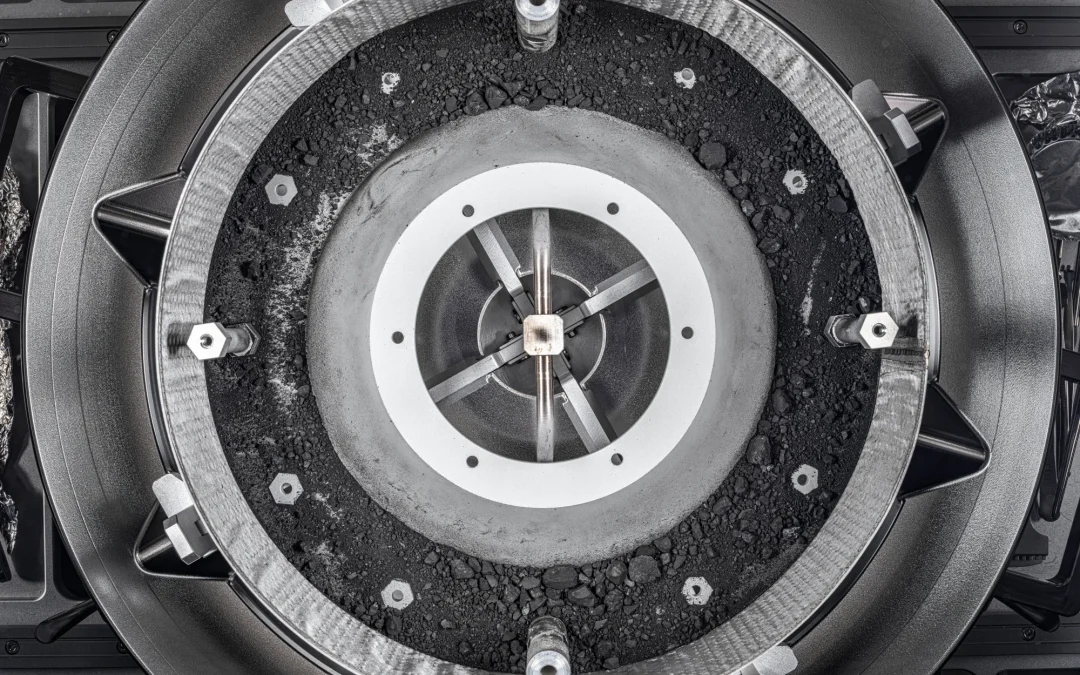

Last week we talked about sample return missions from the Moon and Mars, but scientists have retrieved samples from other objects in the Solar System, including comets and asteroids. What does it take to return a piece of rock from space, and what have we learned so far?

We’ve sent robots to other worlds, but the amount of science we can deploy to another planet can’t compare with the vast science labs we have on Earth. That’s why more and more missions are for a sample return, bringing pieces of alien worlds back to Earth, were we study them with proper equipment.
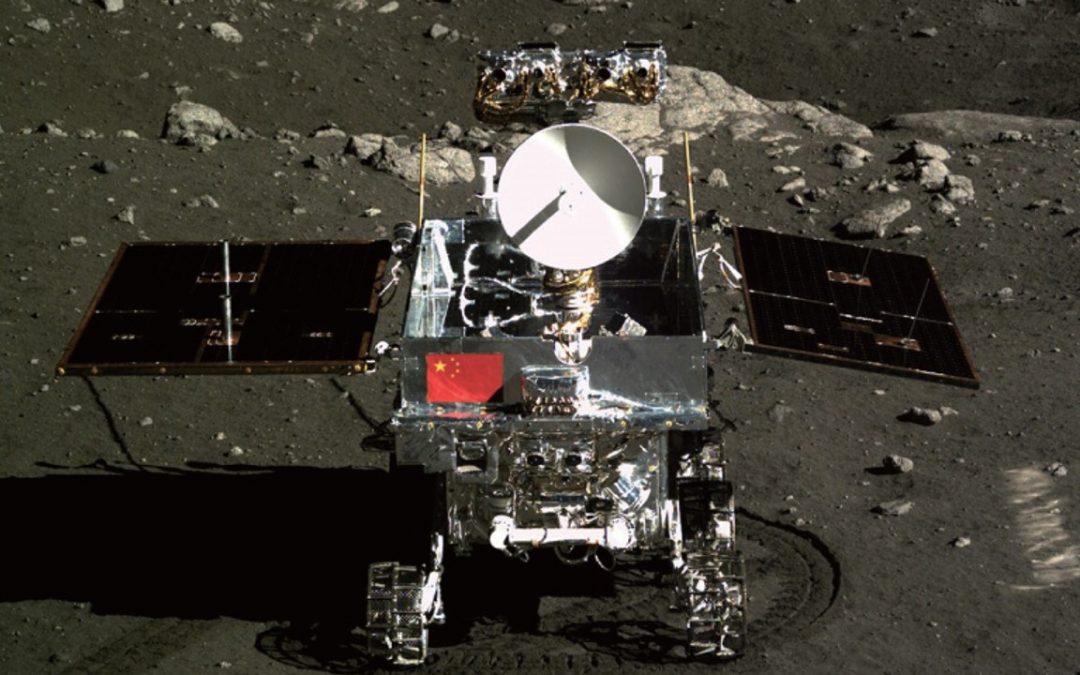

We’re so familiar with NASA’s exploration efforts in space, but you might be surprised to learn that China launches almost as many rockets as the US. They’ve got their own space exploration program that could soon bring humans to the surface of the Moon. Let’s give a brief overview of China’s space exploration plans.

Wherever we find liquid water on Earth, we find life, so it makes sense to search for water across the Universe, and hopefully we can find evidence of life. But what about worlds which are completely covered in water, oceans hundreds of kilometers deep. Can there be too much water?
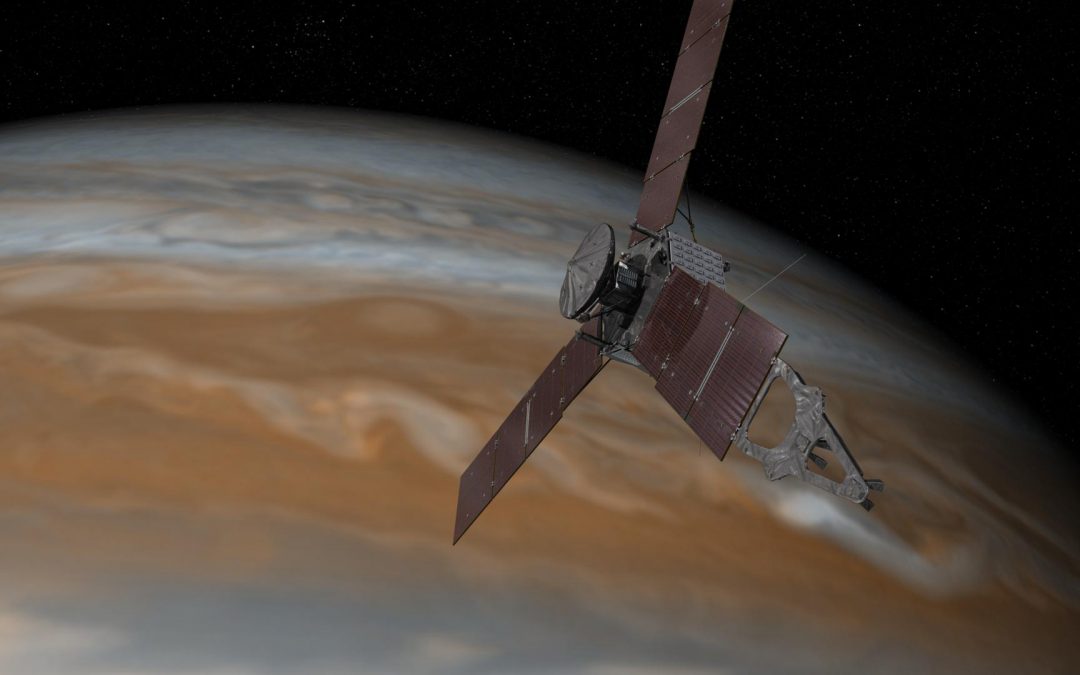

NASA’s Juno spacecraft has completed dozens of flybys of Jupiter, seeing the planet from many angles and delivering some of the most beautiful images we’ve ever seen of the Jovian world. Now it’s focusing in on Io, sending home images of the tiny volcanic world from just 1,500 km away. And the best is yet to come.
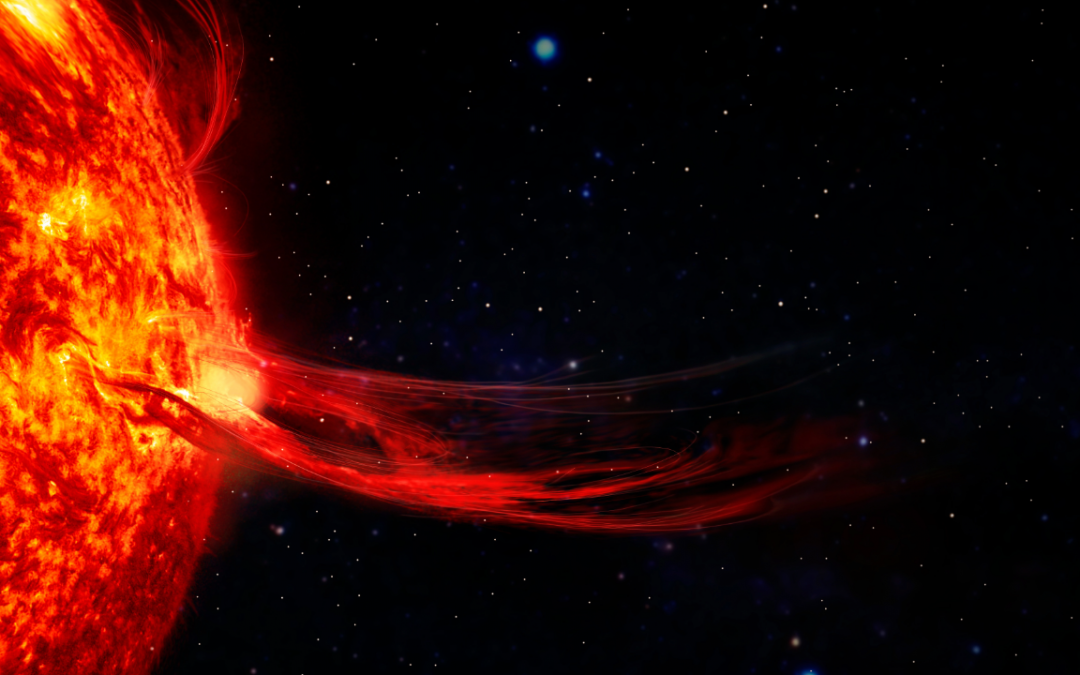

Solar cycle 25 is shaping up to be a doozy, with plenty of flares and coronal mass ejections blasting off the Sun. As the solar activity continues to rise, how are things shaping up?
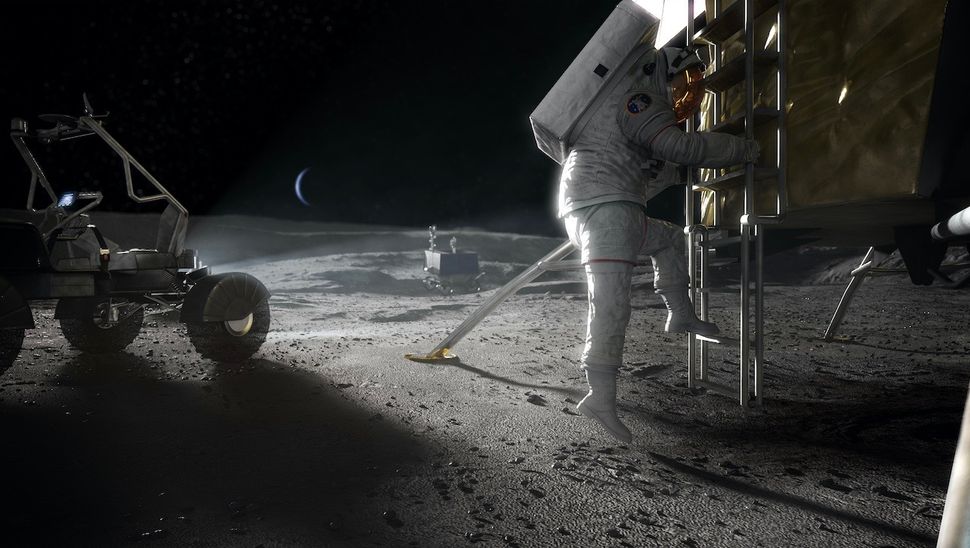

With Artemis 1 completing its robotic flight around the Moon, we know that the SLS works. Next comes Artemis 2, with a crew of astronauts flying past the Moon. If that’s successful, we could see humans set foot on the Moon in December 2025. But there is a long list of challenges to consider that could delay things considerably. Go or no go for launch?

Last week we looked back at some of the ideas that science has changed its mind about. This, we look forward, into the future, at some of the big ideas that astronomers are making progress in. What space science are we looking forward to?

Astronomers talk about all the amazing discoveries they’re making but sometimes, it turns out, they were wrong. After decades and centuries of discoveries, how have they changed their minds?

Just a warning, the holidays are rapidly approaching. It’s time, once again, to think about what to buy all the space nerds on your lists. Here’s what we like.

How the time flies. It’s been over a year since JWST went operational, with other missions joining the fun. What new insights have we gained about the Universe thanks to these powerful new tools?

Finally, we reach the end of our tour through the missions in the Solar System. Out beyond Mars, to Jupiter the Kuiper Belt and Beyond. Recorded live during the CosmoQuestX 2023 Hangout-a-Thon.
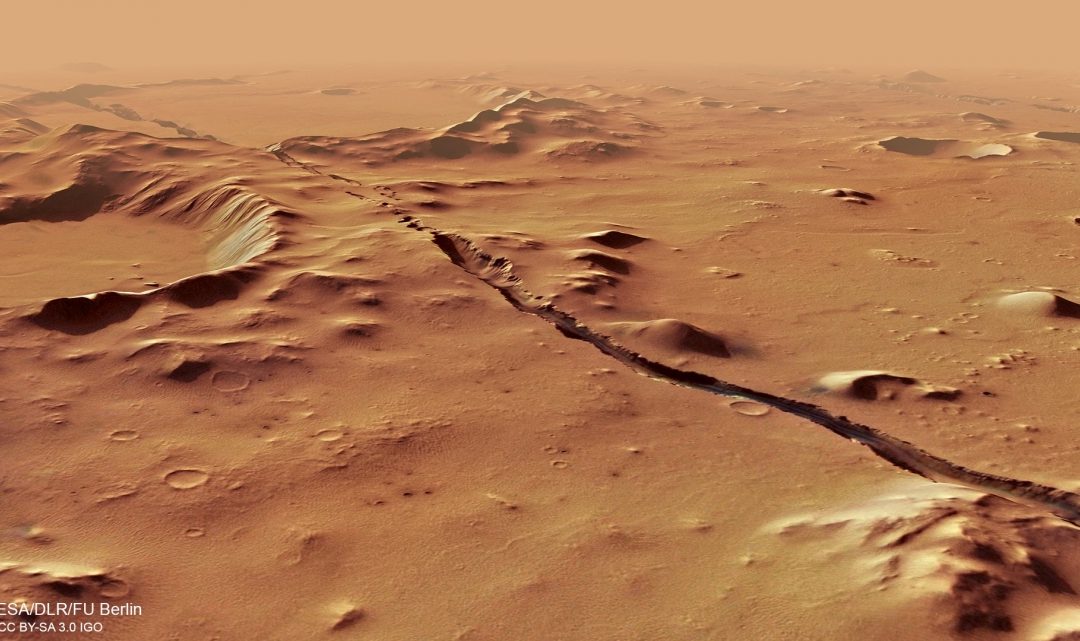
Another week, another review of space missions in the Solar System. Today we set our sights on the red planet. What are all the active missions at Mars today?

Our journey through missions continues, this time we focus on the Moon. There are many nations on the Moon, near the Moon, around the Moon, travelling to the Moon. It’s a lot. We’ll talk about it today.
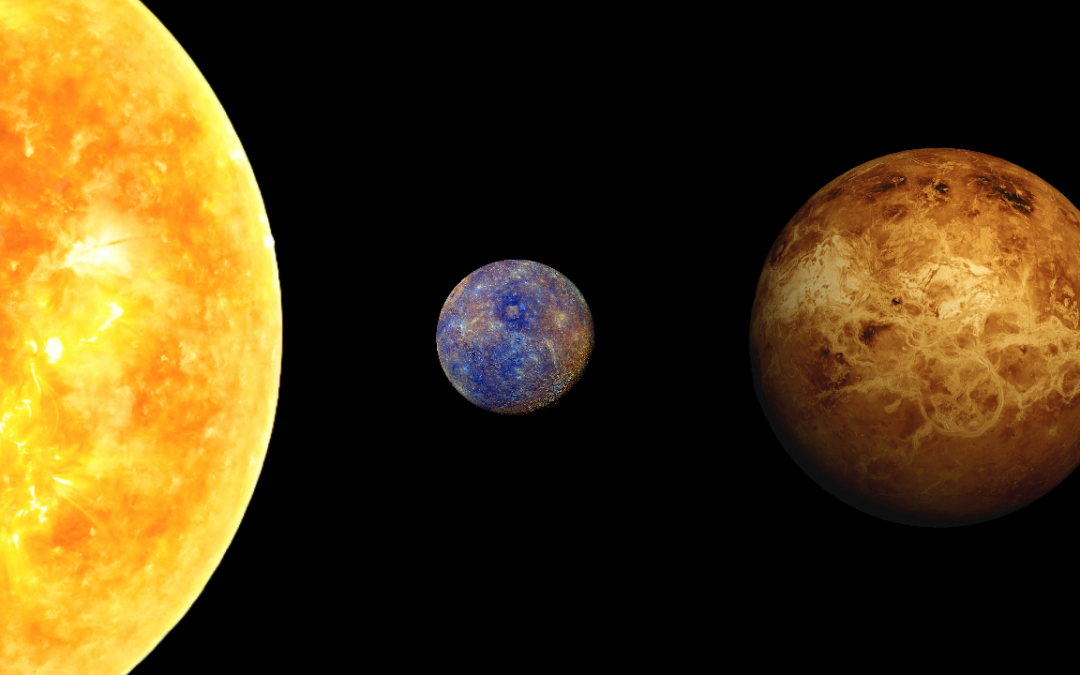
Our journey through space missions continues. Now we move away from the Earth to the rest of the solar system. What’s out there orbiting, roving and flying on other worlds and in interplanetary space. Today we look inward and we’ll talk about the missions studying the Sun, Mercury and Venus.

Last week, we brought you up to speed on the spacecraft which are helping to study Earth from above. Many of our missions are in Earth orbit but looking outward to study the Universe. Today, we’ll talk about the missions close to home, helping us understand our place in the cosmos.

It’s time for another series. This time we’re going to look at the missions that are currently in place across the Solar System. Today we’ll start with the key missions here on Earth, studying the planet from above and looking out into the Universe.
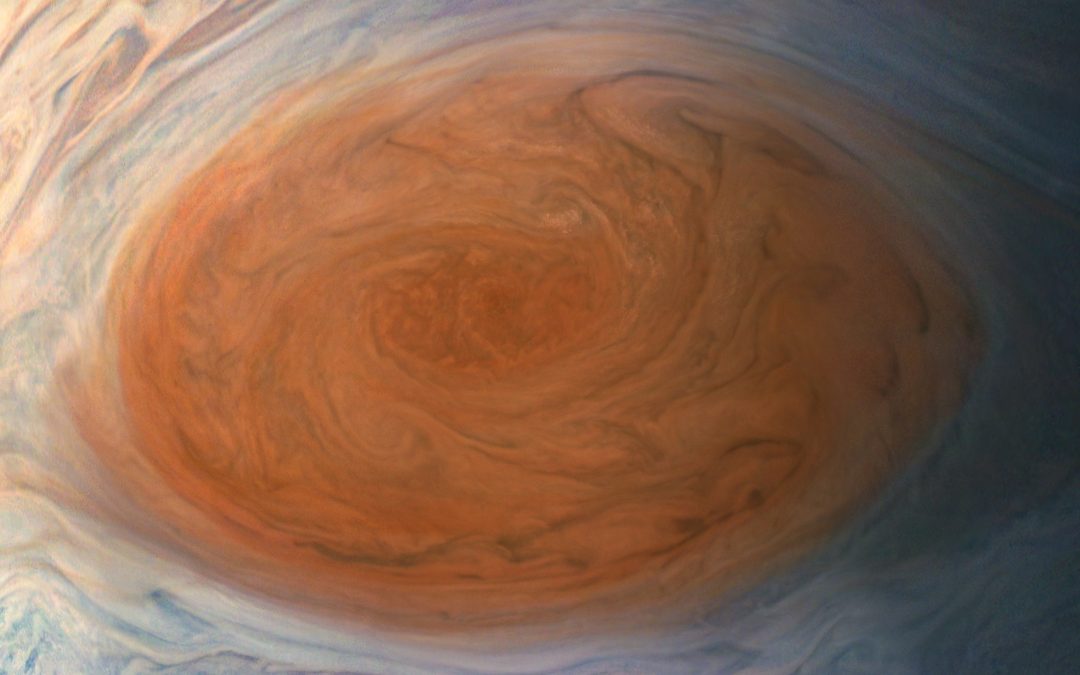

Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is one of its most iconic features, first seen hundreds of years ago. Although it’s certainly long-lasting, it’s been changing in size over the last few decades, shrinking and changing in color. Is it fading away? And what can the changes tell us about storms on giant planets?
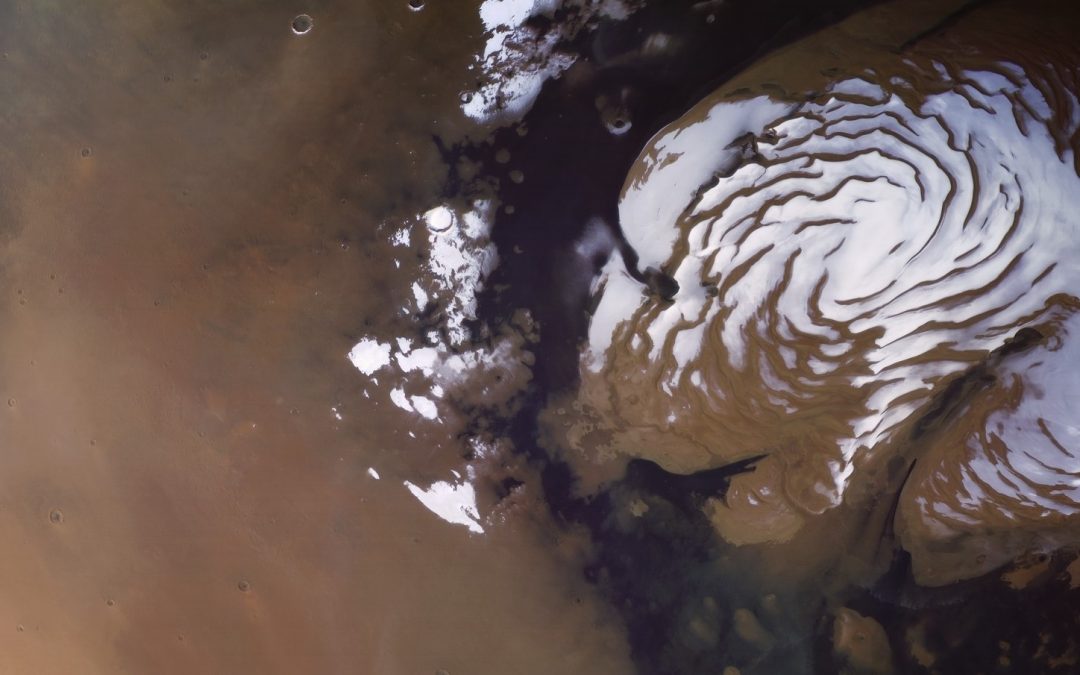

We’ve looked at Earth’s changing climate, now let’s see what it’s like for another world: Mars. Much looks familiar, but some of it is totally alien, from ice caps of frozen carbon dioxide to planetary dust storms that can obscure the entire world from view.